Calcified Coronary Arteries Treatment with PTCA
Coronary artery calcification leads to hardened, narrowed vessels that restrict blood flow and increase cardiac risk. PTCA treatment effectively opens these blocked arteries, restoring circulation and reducing heart attack risk. Our hospital provides advanced technology and expert care, ensuring optimal outcomes in managing calcified coronary lesions through precise and safe interventional techniques.
Causes and Risk Factors for Calcium Deposits in Heart Arteries
Calcium buildup in coronary arteries typically results from age-related vascular changes, chronic inflammation, and lipid accumulation. Major risk factors include high cholesterol, hypertension, diabetes, smoking, and a sedentary lifestyle. Genetic predisposition, kidney disease, and prolonged metabolic disorders also increase the likelihood of arterial calcification, contributing to progressive coronary artery narrowing and blockage.
Symptoms of Calcium Block in the Heart
Patients with calcium block in heart arteries may experience chest pain or discomfort (angina), shortness of breath, fatigue, and reduced exercise capacity. In severe cases, dizziness, palpitations, or sudden cardiac events can occur. These symptoms often signal restricted blood flow and require immediate medical evaluation to prevent heart attacks or other complications.
How We Diagnose Coronary Artery Calcification
Our hospital employs advanced diagnostic tools to detect coronary artery calcification early for accurate treatment planning.
ECG and Stress Test

Electrocardiography (ECG) monitors the heart’s electrical activity to detect ischemic changes, while stress tests evaluate cardiac function during physical exertion. These tests help identify reduced blood flow caused by calcified arteries, indicating the need for further imaging or intervention.
Coronary Calcium Score (CT)
A non-invasive CT scan measures the extent of calcium deposits in coronary arteries, producing a coronary calcium score. This score predicts the risk of coronary artery disease and guides preventive or therapeutic strategies to manage calcified blockages effectively.
IVUS (Intravascular Ultrasound)
IVUS involves inserting a small ultrasound probe into the coronary arteries, producing cross-sectional images of the vessel walls. It precisely assesses the amount and distribution of calcium, aiding interventional planning for procedures like PTCA in calcified lesions.
OCT (Optical Coherence Tomography)
OCT uses near-infrared light to generate detailed images of the coronary artery's inner layers. This technique helps identify the thickness, location, and severity of calcified plaques, allowing cardiologists to choose the most effective treatment approach during PTCA.
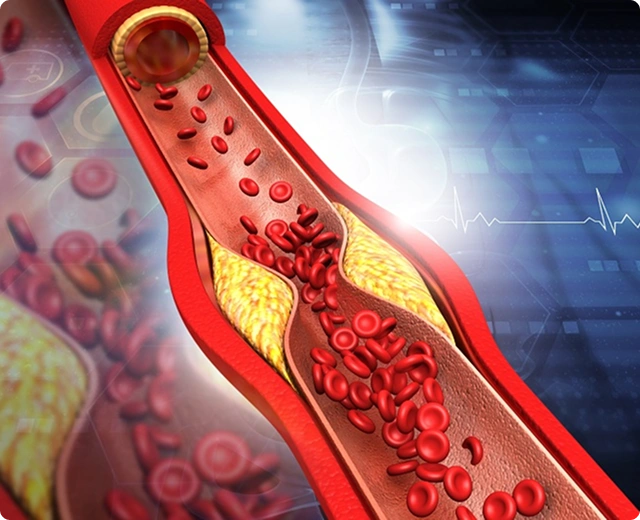
Managing Calcified Arteries with PTCA
Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty (PTCA) is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat calcified coronary artery blockages, restoring proper blood flow. Treatment strategies are tailored based on calcification severity and lesion characteristics, ensuring precise intervention. Techniques such as specialized balloons, rotational or orbital atherectomy, and cutting-edge stent placement are chosen accordingly. This customized approach optimizes procedural success, reduces complications, and enhances long-term vessel patency in patients with complex calcified coronary lesions.
Advanced TreatmentTechniques We Offer
Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty (PTCA) for calcified coronary lesions requires technique selection based on calcification severity and lesion complexity to ensure safe plaque modification and optimal stent placement.
NCB (Non-Compliant Balloon Angioplasty)
NCB angioplasty uses a high-pressure balloon designed to dilate rigid calcified plaques. This technique ensures effective lesion expansion when standard balloons fail, minimizing the risk of vessel recoil. It is ideal for resistant, moderately calcified segments needing precise luminal enlargement before stenting.
ROTA (Rotational Atherectomy)
Rotational Atherectomy involves a high-speed rotating burr that selectively sands down calcified plaque without damaging healthy vessel walls. This technique prepares heavily calcified or undilatable lesions, creating a smoother path for balloon angioplasty and stent placement, especially in complex coronary anatomies.
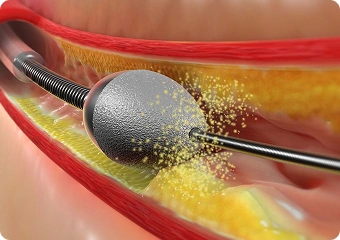
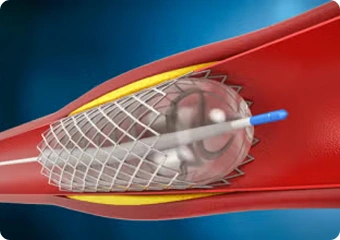
Cutting Balloon Angioplasty
This method employs a balloon equipped with microblades that create controlled incisions in calcified plaque upon inflation. It effectively fractures tough calcific deposits, enhancing lesion compliance and facilitating better stent expansion in areas where standard balloons cannot achieve sufficient dilation.
IVL (Intravascular Lithotripsy)
Intravascular Lithotripsy delivers sonic pressure waves that crack calcium within the arterial wall, making it more compliant. This technique ensures uniform balloon expansion and optimal stent deployment, particularly useful in concentric, deeply embedded calcifications resistant to other plaque-modification strategies.
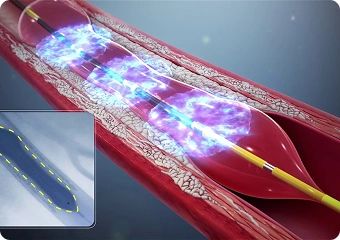
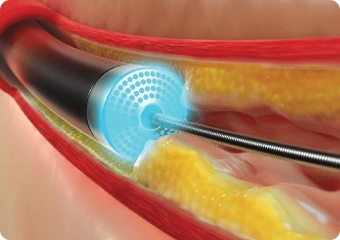
Laser Angioplasty
Laser angioplasty vaporizes calcific and fibrotic plaque using controlled laser energy, creating a clear passageway through occluded segments. This method is reserved for select complex lesions, offering precise plaque removal without damaging surrounding tissues, thus aiding balloon and stent delivery.
Why Choose Us for Calcified Coronary Treatment
Expertise in Complex Coronary Interventions
Extensive experience in treating severely calcified coronary lesions with specialized PTCA techniques.
Advanced Equipment
Use of the latest technologies, including ROTA, IVL, Laser Angioplasty, IVUS, and OCT for precise plaque modification.
Multidisciplinary Cardiology Team
Collaborative care approach involving interventional cardiologists, imaging experts, and cardiac surgeons.
Patient-First, Safety-Focused Approach
Individualized treatment plans ensure maximum safety, effectiveness, and faster recovery.
Comprehensive Diagnostic Support
Detailed pre-procedural assessment using advanced imaging tools to guide accurate and safe interventions.
Post-Procedure Monitoring
Structured follow-up programs to track recovery, prevent complications, and ensure long-term success.
Our Locations
Discover morefrequently asked questions
-
Advanced techniques like PTCA with ROTA, IVL, or Laser Angioplasty are preferred for treating severe calcified coronary lesions. Treatment choice depends on the severity and complexity of the blockage. Accurate imaging guides precise intervention.
-
There is no difference; PTCA (Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty) is the technical term for coronary angioplasty. Both describe the procedure of opening narrowed coronary arteries using a balloon. Stent placement often follows angioplasty.
-
Complete removal of arterial calcium naturally is not possible. However, lifestyle changes like a healthy diet, exercise, and smoking cessation slow disease progression. Medications also help manage risk factors.








